

The purpose of the risk management framework is to assist the organization in integrating risk management into significant activities and functions. The effectiveness of risk management will depend on its integration into the governance of the organization, including decision-making. This requires support from stakeholders, particularly top management. Framework development encompasses integrating, designing, implementing, evaluating and improving risk management across the organization. Ref: ISO 31000:2018 Framework

.png)
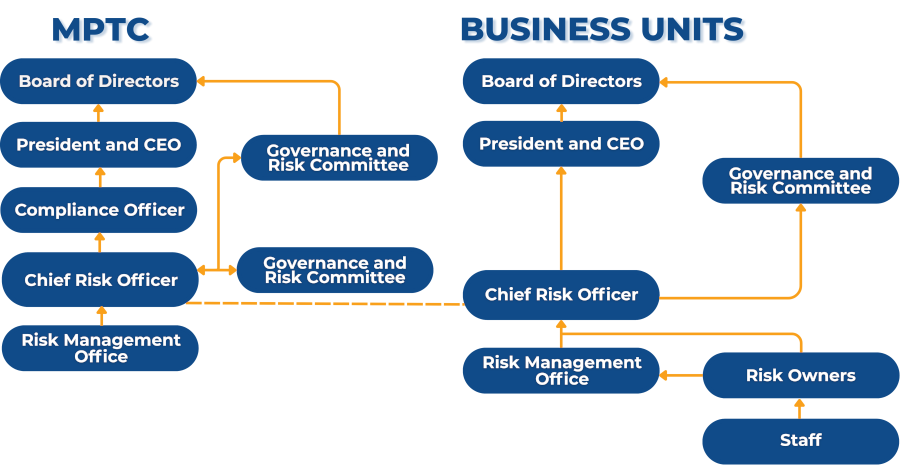
GOVERNANCE AND ACCOUNTABILITIES IN MANAGING RISKS
- Board of Directors through the Corporate Governance and Risk Committee - Shall oversee and ensure the development and adoption by Management of an Enterprise Risk Management Plan. Oversee management's efforts in identifying and managing its risks; Provides assurance that a risks management process is in place and that risks are periodically identified, assessed and controlled.
- President and CEO - Ensures that risk management is embedded in the organization in all decision-making processes and activities. Ensures the creation of a risk management culture across the entire organization.
- Chief Compliance Officer (CCO) - Ensures compliance is embedded in the organization, aligning compliance strategies with the organization's risk management efforts, and providing sound recommendations to mitigate risks and non-compliance.
- Chief Risk Officer (CRO) - Ensures that risk management is embedded in the organization's risk management efforts and activities. Ensures that the organization conforms and complies with the risk management strategies set by the management. Reports the risk identified, controls in place and makes sound decisions and recommendations.
- Internal Audit - Shall develop risk-based internal audit programs. It shall audit the risks processes across the organization. It shall regularly prepare and submit reports to the management and Audit Committee with regard to the efficiency and effectiveness of internal controls.
- Enterprise - Wide Risk Management Office- Formulate the strategy and the policy based on risk appetite, risk attitudes and exposures; Receive risk reports from departments and business units; Review risk management activities and compile the organization's risk register in preparation of risk report. Risk reports shall be reported and presented to the Chief Risk Officer (CRO). Track risk management activities and keep the risk management context under review.
- Risk Owners - Monitors, manages, report risk associated with their processes, department/ business units. Prepares and updates risk register and risk treatment plan. Set risk priorities and exploit opportunities.
RISK MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK
MPTC's risk management framework is a set of components that provides the foundations and organizational arrangements for designing, implementing, monitoring, reviewing and continually improving risk management throughout the organization. MPTC is committed to maintaining an effective, efficient and customized risk management framework that consists of:
- a Risk Management Policy;
- a Risk Management Plan and supporting policies that complement risk management such as but not limited to, fraud prevention, business continuity management, occupational health and safety management systems and code of conduct, etc.
The framework will enable:
- a formal, structured approach to risk management that is appropriate to the organization's activities and operating environment;
- a risk management approach consistent with the principles of the Enterprise Risk Management- ISO 31000:2018 (en) Risk Management Guidelines.
MPTC ERM and its framework is concerned with:
- Strategic Risks - risks associated with long-term organizational objectives and the means by which those objectives will be achieved.
- Operational Risks - risks associated with the development and implementation of operational plans. These Risks are associated within the normal business functions. Should be managed and assessed by the business units to which they are identified, which may also include climate change physical risks, such as extreme heat, cyclones or typhoons, increased precipitation or heavy rainfall.
- Financial Risks - Defined as those risks whose principal effect would be a financial loss or lost opportunity to deliver financial gain.
- Legal and Compliance Risks - Risk associated with the adherence of applicable laws, rules and regulations. Entails some regulations from government, which may include specific regulations related to climate risk management and environmental compliance.
- I.T./Technology Risks - Are any potential technology failures that disrupts a business, such as but not limited to information security incidents which may have implications for data related to climate risk assessments.
